MOR-PROC-027 Version 1 Last Review Date: Nov, 2024
APIm (Public API)
1. Overview
The MoreCore Public API utilises a Microsoft APIm service frontend 'Public API'. It consists of:
- The main 'MoreCore Platform' DevOps Project (MoreIQHoldings org)
- GIT Repo
- The 'CMMS APIManagement' DevOps project (cbc-melb org)
- GIT repo
- Azure APIm Service (Azure)
- Developer Portal
- Gateway? TBC
1.1. 'MoreCore Platform' DevOps Project - REST API
The main MoreCore Platform project has the code that actually handles the requests and responses (i.e. the REST API Backend), which the APIm frontend connects to.
Part of this code is produced by a code generator. As a rule of thumb, any extensions to the REST API that are generic enough should be implemented in the code generator templates, rather than as extensions to classes produced by the code generator.
The code generator produces several types of classes involved in handling the REST API operation, based on convention and decorators applied to domain objects:
- DTO objects
- These objects define the data schema for the REST API.
- Validators
- These objects are used to define validation rules for REST API write operations.
- Services
- These include low-level services that communicate with the database, map incoming and outgoing data and perform business logic.
- REST API Controllers
- This is the top layer that exposes REST API contracts to outer world and utilizes lower-level services to perform operations.
Classes produced by code generation support extension points, normally via partial methods or class overrides, that enable their behaviour to be tweaked, while still allowing for most of the generated code to be re-used.
"Code generator" consists of multiple T4 templates (one for each type of class generated). Generation process is run by running the T4 templates - Visual Studio can be configured to run all the templates in pre-build stage or templates can be run manually*. The usual development process is to run them manually, immediately after the domain model has been changed, as the development approach is full-stack (i.e. the same developer builds the entire vertical structure of the component).
*Manually running a T4 template from within Visual Studio means either simply saving the file (Crtl+S) or right-clicking on the template file and selecting the "Run Custom Tool" operation.
Code generator T4 templates are located within the CodeGen project (PMMS/CodeGen). Each project in the solution that needs to have files that are code generated has a dedicated folder within the CodeGen project (named identically to the target project). In regards to the REST API, the following T4 templates are of importance:
- PMMS.Business.Portal folder
- Service.tt - generates services that communicate with database and perform business operations. Used by all APIs and other system components, not just the REST API. Outputs generated files into Services folder of the PMMS.Business.Portal project.
- RestService.tt - generates services that perform REST operations specifically. Most of this operation is delegated to business services described in the previous bullet point. Outputs generated files into Services/REST folder of the PMMS.Business.Portal project.
- PMMS.Services.DataAccess folder
- DTOv2.tt - generates DTO classes that compose the REST API data schema, but also other API data schemas (i.e. not limited to REST API data schema). The resulting DTO class hierarchy is somewhat more complex than might be expected due to the necessity to support multiple disparate APIs, while still making it possible to use the same underlying services. Outputs generated files into DTO folder of the PMMS.Services.DataAccess project.
- NamebookDTO.tt - similar to previous bullet point, except that produced objects are simplified down to bare bones and contain only the basic info about the object, such as ID, Name, Code etc. Outputs generated files into DTO folder of the PMMS.Services.DataAccess project.
- DTOValidator.tt - generates classes that handle validation for input data represented with DTO objects. Outputs generated files into Validation folder of the PMMS.Business.Portal project.
- PMMS.Web.ClientPortalApi
- RestApiController.tt - generates REST controller classes. Controllers are the top-level layer that communicates directly with the APIm and all operations are routed through them.
1.2. 'CMMS APIManagement' DevOps Project
Variables
Pipelines
CMMS APIManagement Publish
CMMS APIManagement Extract
General Pipeline Actions
Checkout
- x
Extract ??
- x
Run Spectral Lint
- x
Publish
Checkout
Download Artifacts
Create Pull Request
Postjob
GIT Repo
1.3. Azure APIm Service
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/api-management/ (opens in a new tab)
1.3.1. Developer Portal
The APIm Developer Portal is an interface for providing access to integration developers so they may browse the available API endpoints, see the request/response requirements, field requirements etc.
It includes:
- A list of available endpoints
- Detail view of each endpoint
- Request structure
- Required HTTP headers
- Request body
- Response body
- Example Request/Response
- Export buttons to produce YAML/JSON output
- 'Try It' button to actually run API calls.
See section 4 of this document for steps to onboard a user to the APIm developer portal.
TODO: image
2. Environments
2.1. Production
Azure Resource
Connected environment: Prod (cmms.cbcgroup.com.au)
Developer Portal
As this instance is connected to Prod, the developer portal is off for this instance.
2.2. Test
Connected Environment: cbc-post
3. Development Process
Decide on changes
Edit the code
- tbc
Run the code generators
- tbc
Deploy code to CMMS enviro
Run APIm pipelines
- x
- x
Confirm changes
Code generation process?
BM: I understand that all of some of the code for this project is generated. More understanding needed.
GIT Repo
Code for the APIm instance is stored here: https://cbc-melb.visualstudio.com/CMMS%20APIManagement (opens in a new tab)
Build Pipeline Overview
The DevOps GIT Repo includes a wiki page for the Promotion workflow: https://cbc-melb.visualstudio.com/CMMS%20APIManagement/_wiki/wikis/CMMS-APIManagement.wiki/1/Promotion-workflow (opens in a new tab)
4. APIm User Management
To enable a user to access the API, some setup steps are required:
5. Producing the OpenAPI schema and updating APIm
The APIm service is configured by uploading an OpenAPI schema (v3 schema specifically), which means that this schema needs to be produced from the REST API code and data model. At the moment, this process is somewhat convoluted, as it includes running Swagger to produce a v2 JSON schema, then converting that schema into YAML/v3 schema and adding examples. The exact process is described below.
Make changes
- In this step any changes to data model and business logic are implemented, code generators are run and any necessary extensions are implemented.
Extract OpenAPI v2 JSON schema
- In order to extract the v2 JSON schema, API project (PMMS.Web.ClientPortalApi) needs to be started. This opens the Swagger UI. The raw schema is (usually) at http://localhost:5000/swagger/docs/v1 (opens in a new tab).
Convert OpenAPI v2 JSON schema into OpenAPI v3 YAML schema
- At the time of implementation, there was no good library to automate this internally, so an external service is used for this. Raw schema from the previous step is copied and service at https://editor-next.swagger.io/ (opens in a new tab) used to convert to desired format:
- Paste the raw v2 schema into the editor window
- The service automatically offers conversion to YAML - clicking OK converts the schema
- Edit -> Convert to OpenAPI 3.0.x converts the v2 schema into v3 format
- x-original-swagger-version field at the bottom needs to be manually removed (space for improvement - could be removed in the next step programmatically)
Utilize unit test to add examples to the generated schema
- The project PMMS.Web.ClientPortalApi.Tests contains the REST API examples - RestApiTests/Data/ RestApiExamples.txt. This file is used to incorporate examples into the REST API schema:
- The file is edited manually as needed to add new examples
- Test class RestApiTests/AddExamplesToOpenAPISpecification.cs is used to combine the raw OpenAPI v3 YAML schema with the examples file to produce the final schema with examples by running the ParseYamlOpenAPIFileAndAddExamples method.
- In order for it to be ran properly, fields inputFilePath and outputFilePath within the test class need to be adapted as necessary.
- The final OpenAPI v3 YAML schema with examples is then ready to be uploaded to APIm
Create new revision in APIm
- Revisions are accessed via APIm service in the Azure portal -> APIs -> [specific API] -> Revisions tab in Azure Portal
*
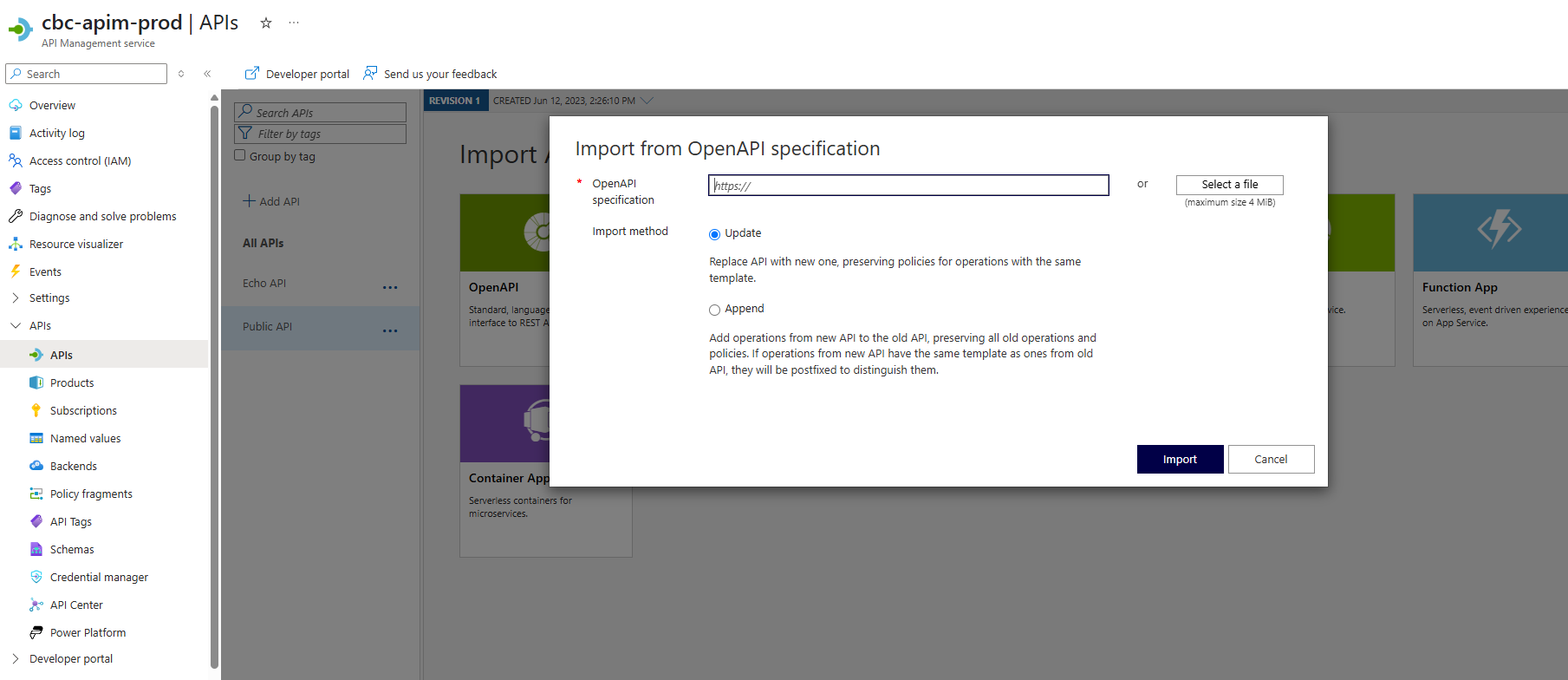
- After creating the new revision - schema is uploaded by clicking on the menu of the specific API, selecting Import, then Open API and selecting the file produced in the previous step
- Import method used needs to be Update (default)
Test and make the latest revision current
- After testing the new revision (on its separate revision URL), the newly added revision can be made current in the Revisions tab from previous step
6.0 Migrate to Production
Export the APIm definition from Test
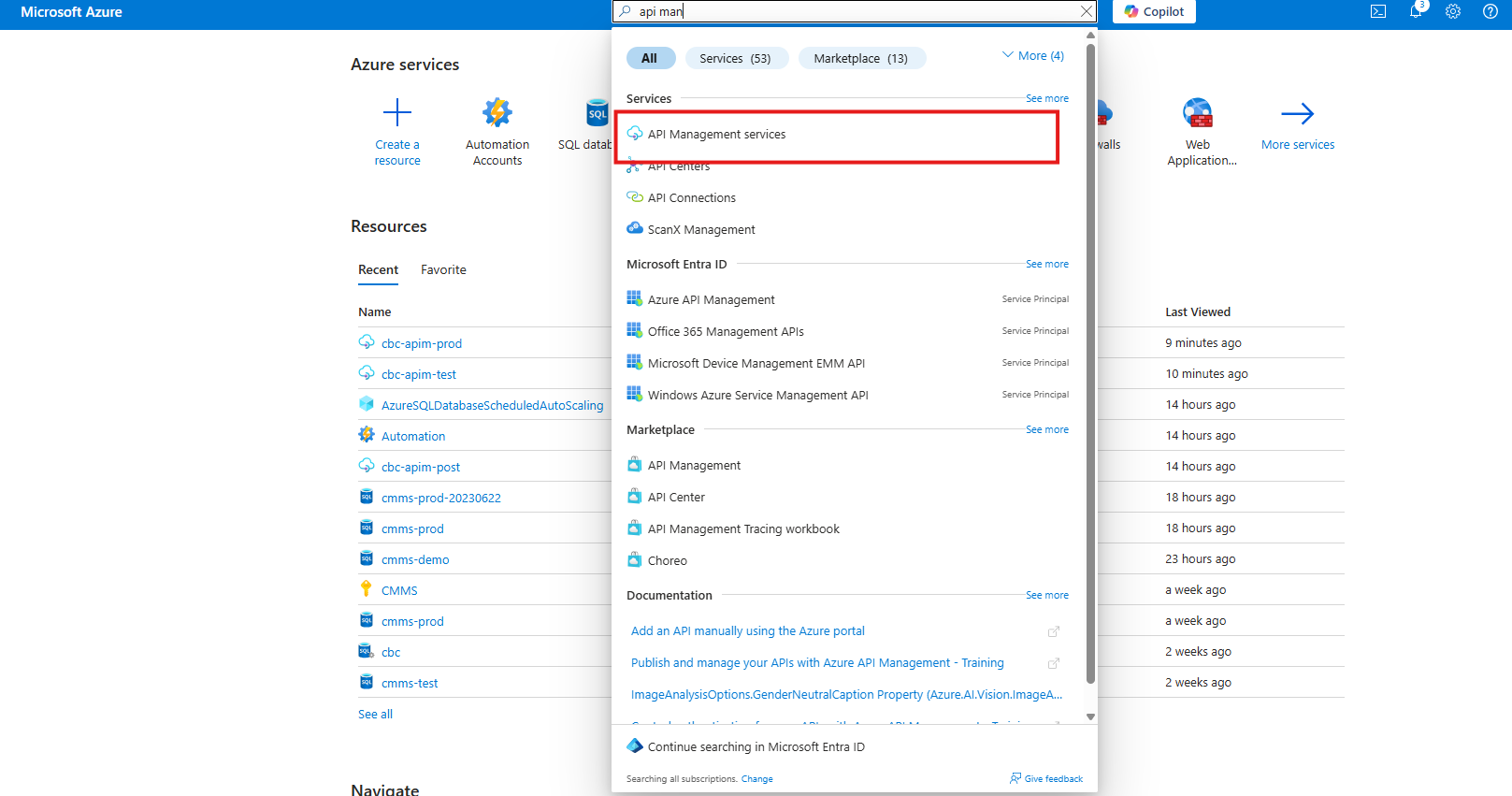
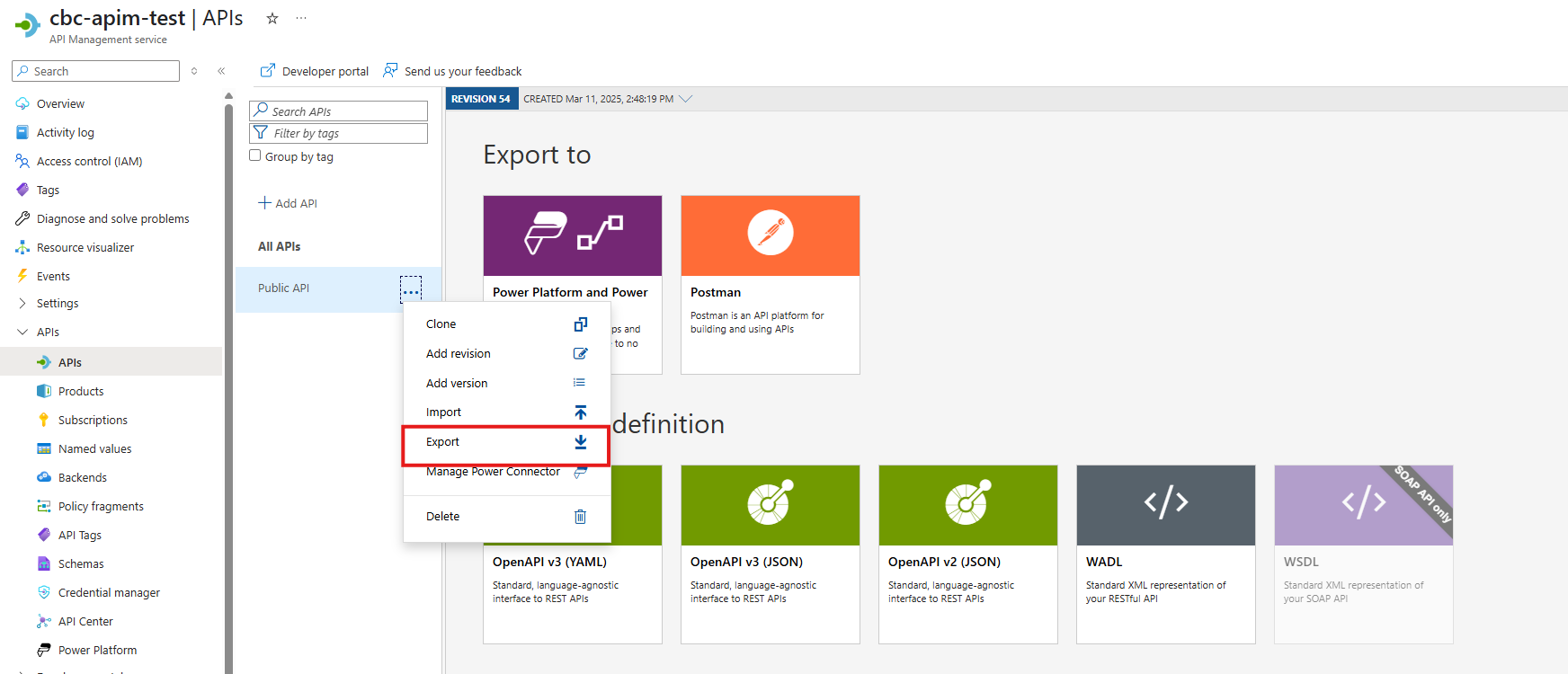
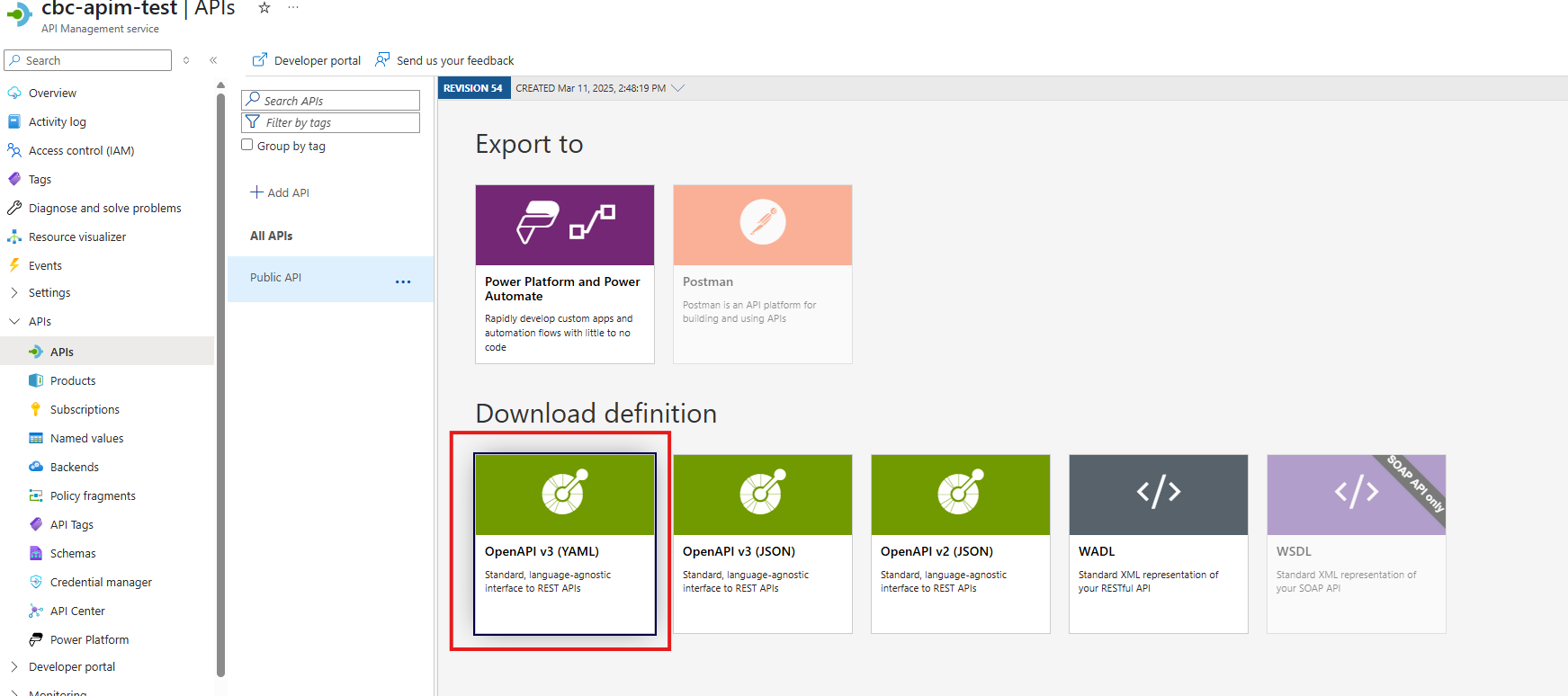
Select the Production APIm Instance

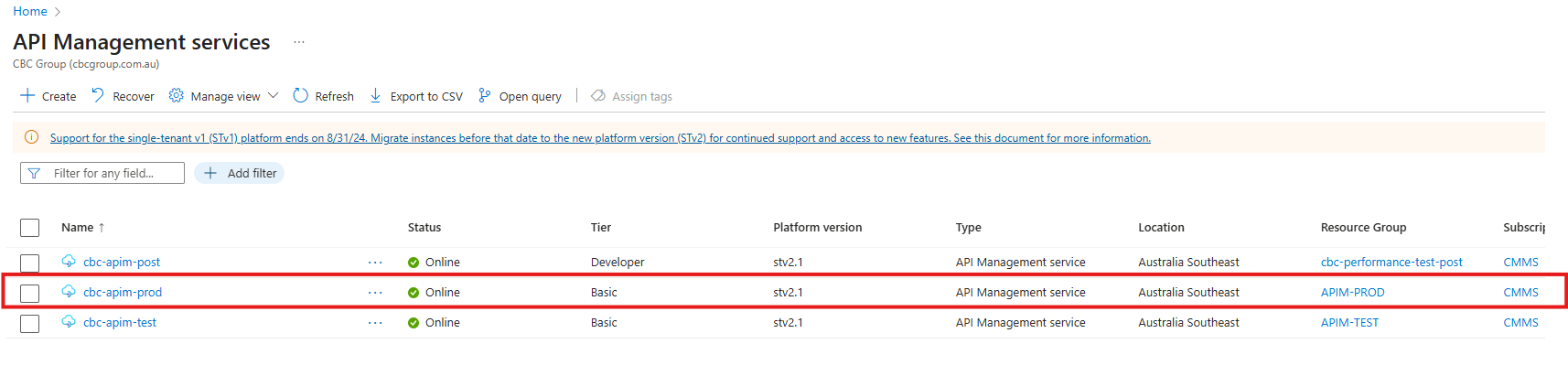
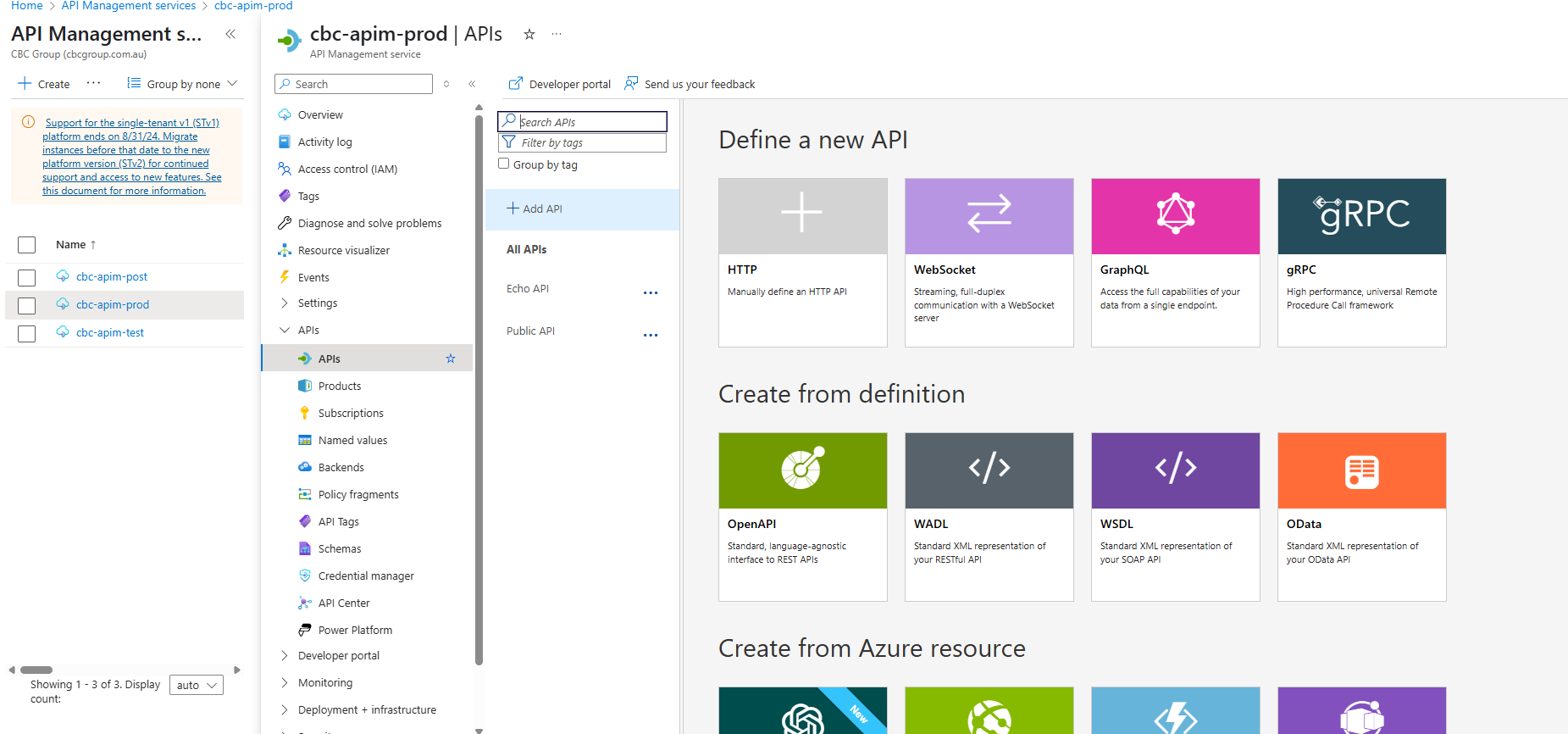
Export a copy of the current Production APIm Definition
- This will be used in case you need to roll back your changes.
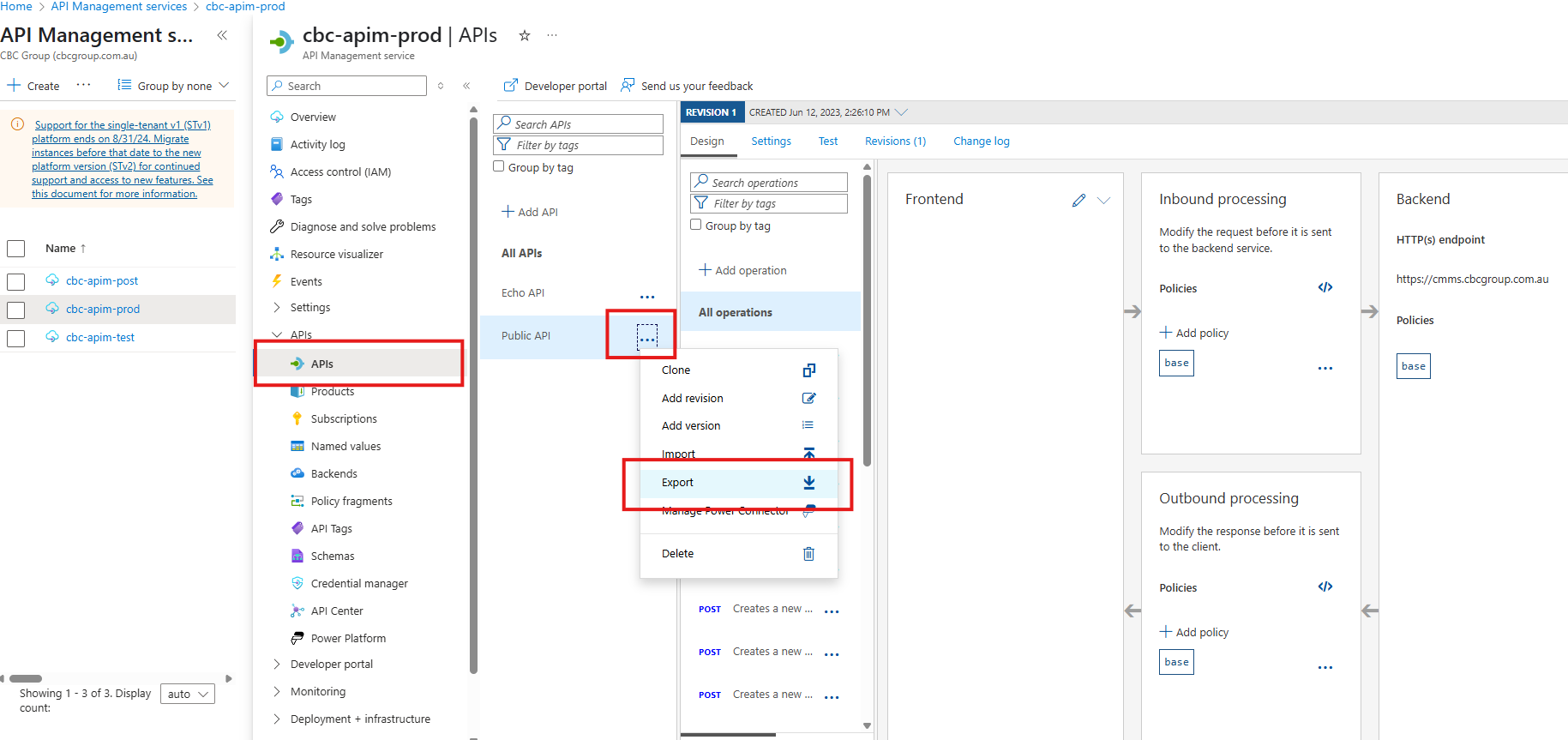
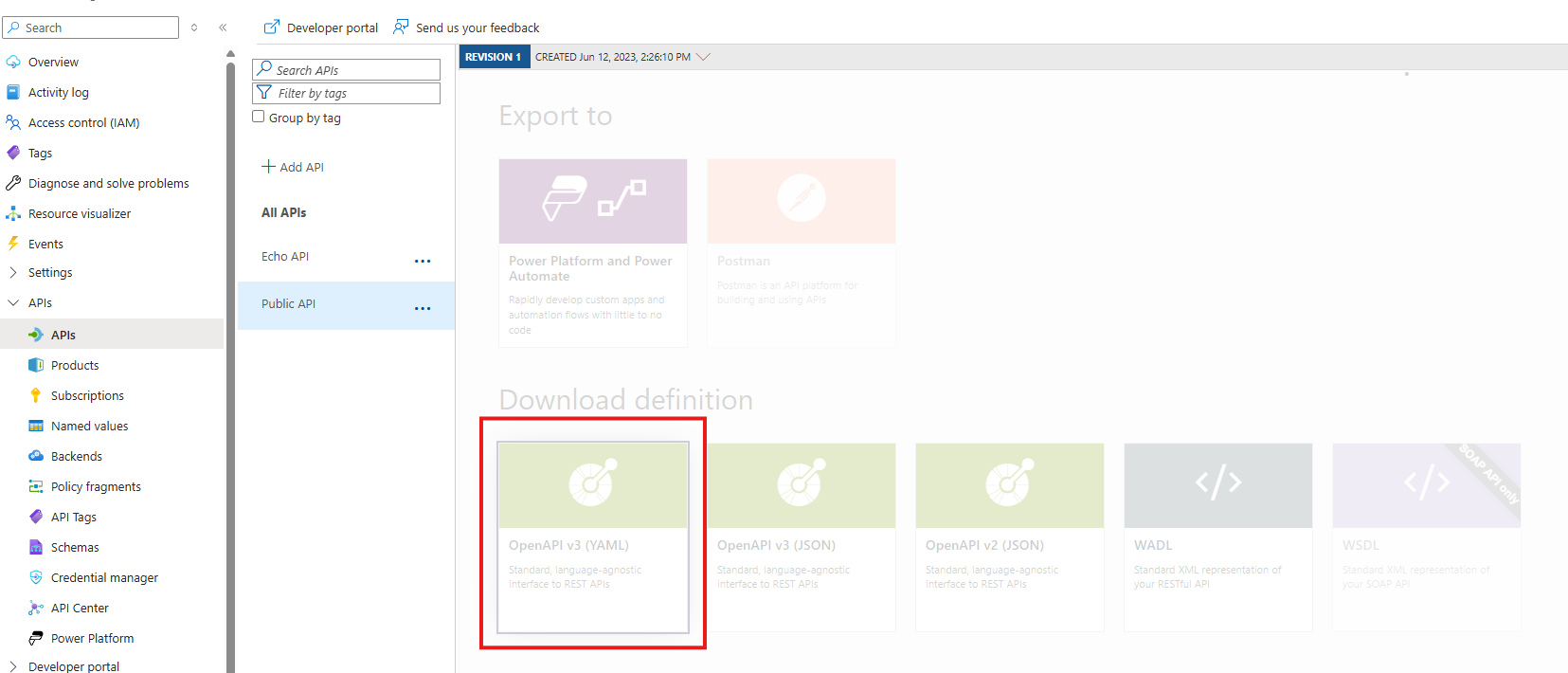
Import the Test Definition performed in Step 1.
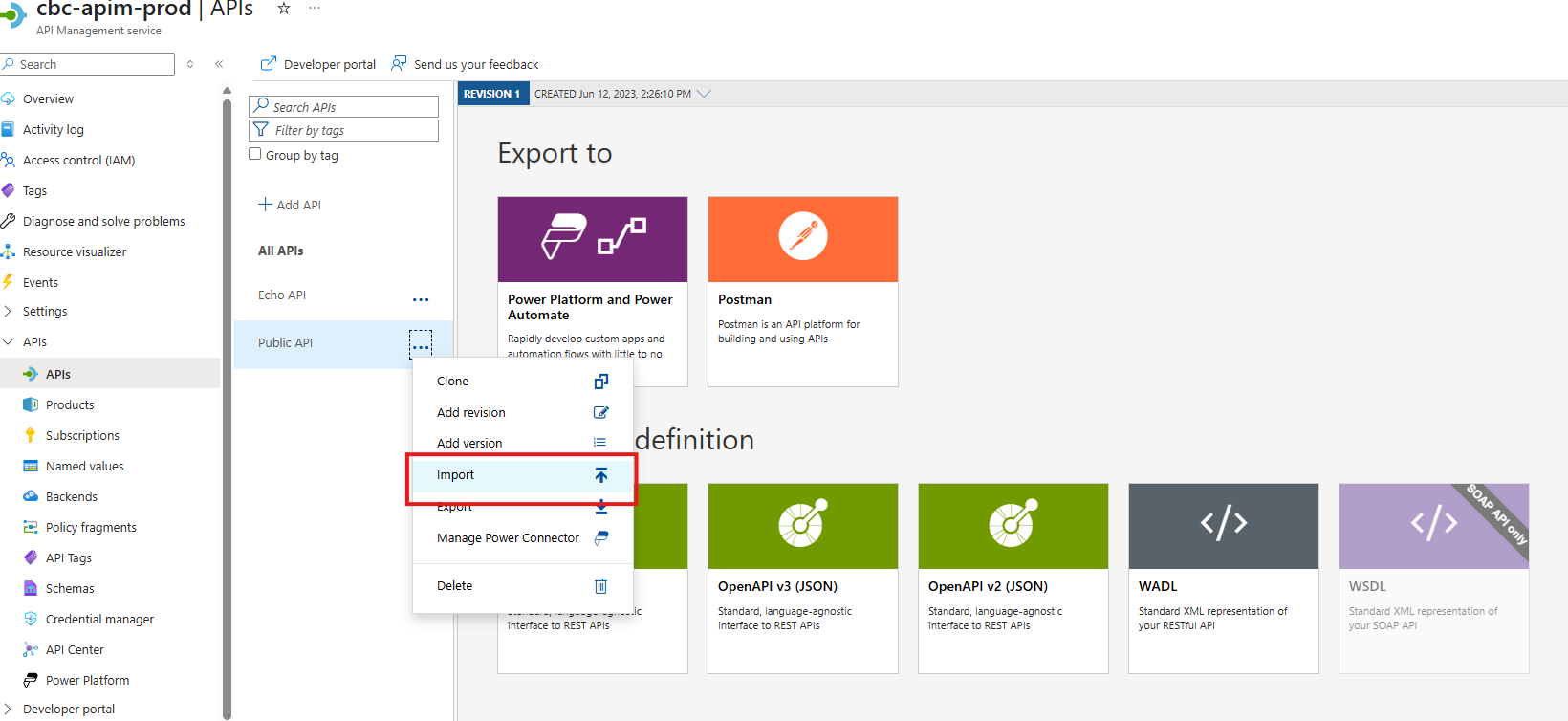
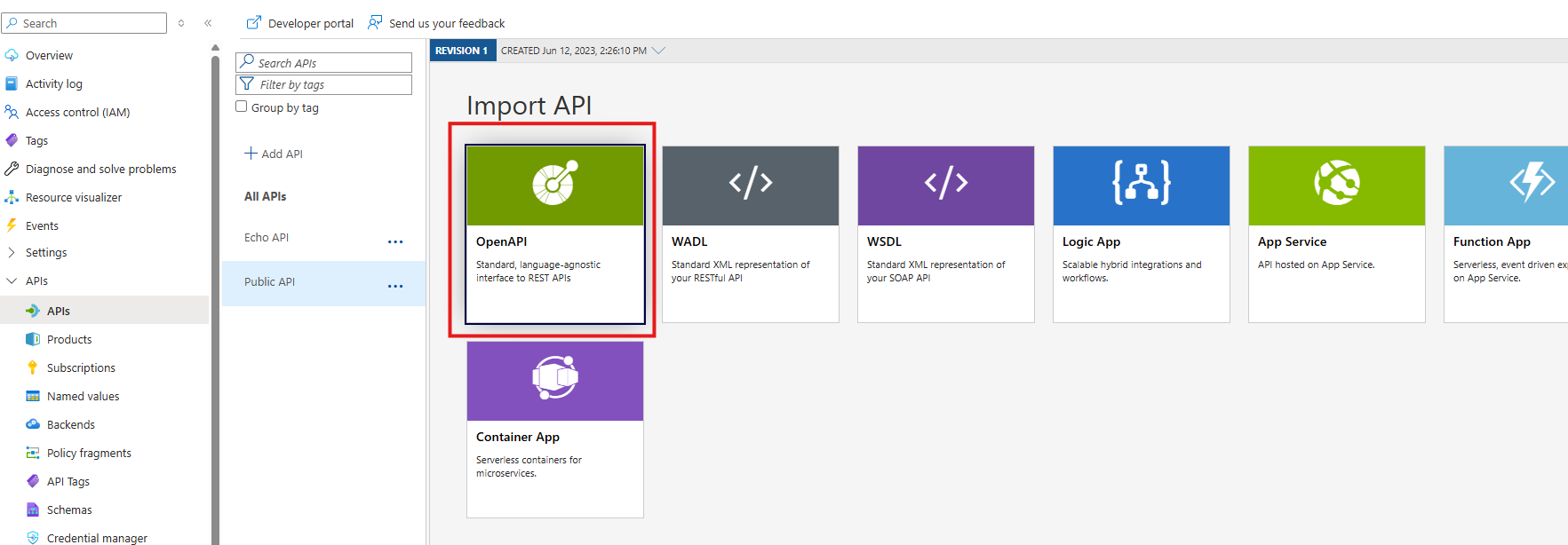
Change the Settings Once Imported
- You will need to change the Web Service URL for production to https://cmms.cbcgroup.com.au (opens in a new tab)

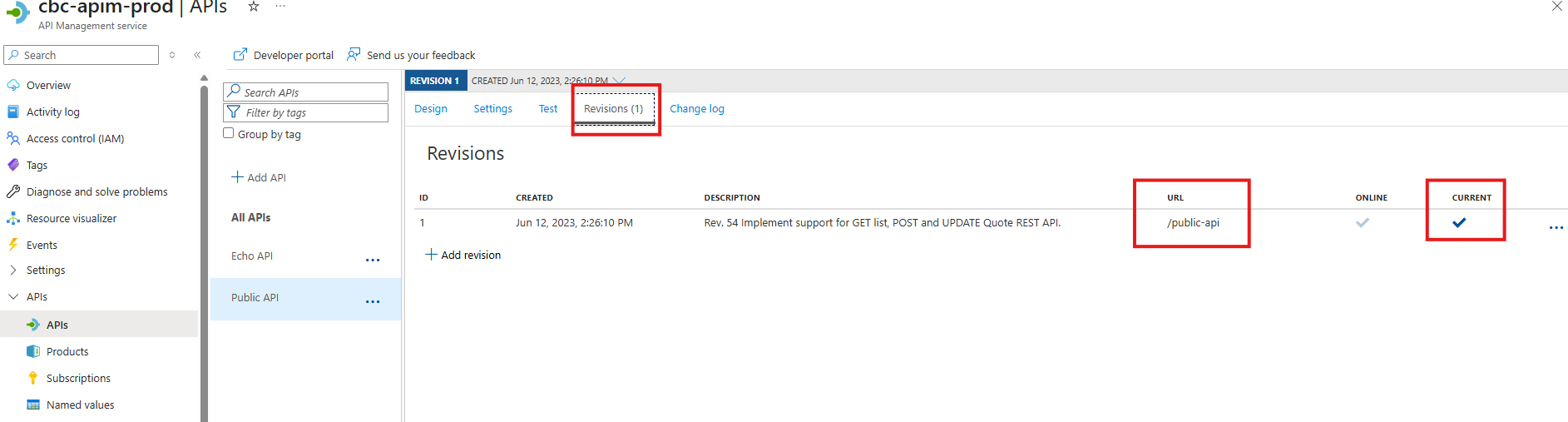
Update the Webservice URL
- Ensure the URL is /public-api
- Current is ticked
- APIm allows multiple versions. Each version can be reached by addressing the appropriate revision by adding ;rev=xx where xx is the revision. ie. /public-api;rev=53 (this will be the end point for revision 53)
It is important that the current API has NO rev=xx where xx is the revision. ie. /public-api ONLY
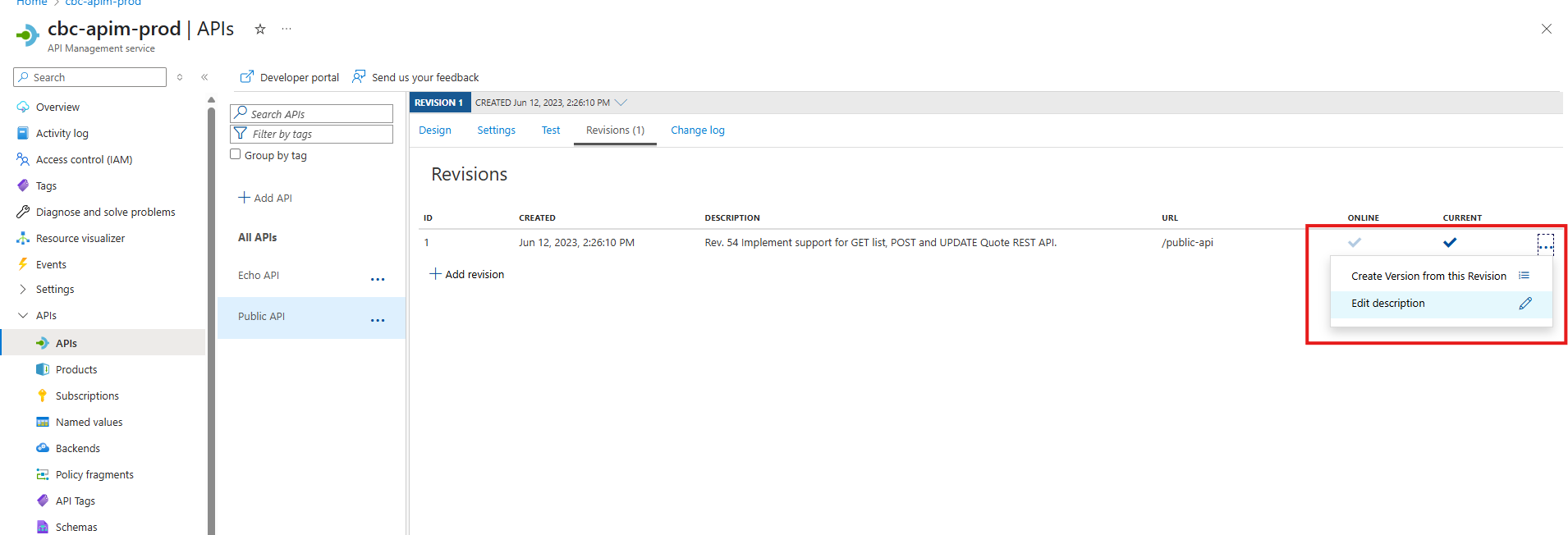
Change the revision Description
- Change the description to match the version you have imported
Confirmation API's are working
-
You can look into the Analytics (classic). This will show if API's are being called and give an overall view.
-
You should still perform a API call to ensure that the API's are reachable and performing correctly. Use APIdog, Boomi or Postman to perform a sample call.
-
To Use Boomi.
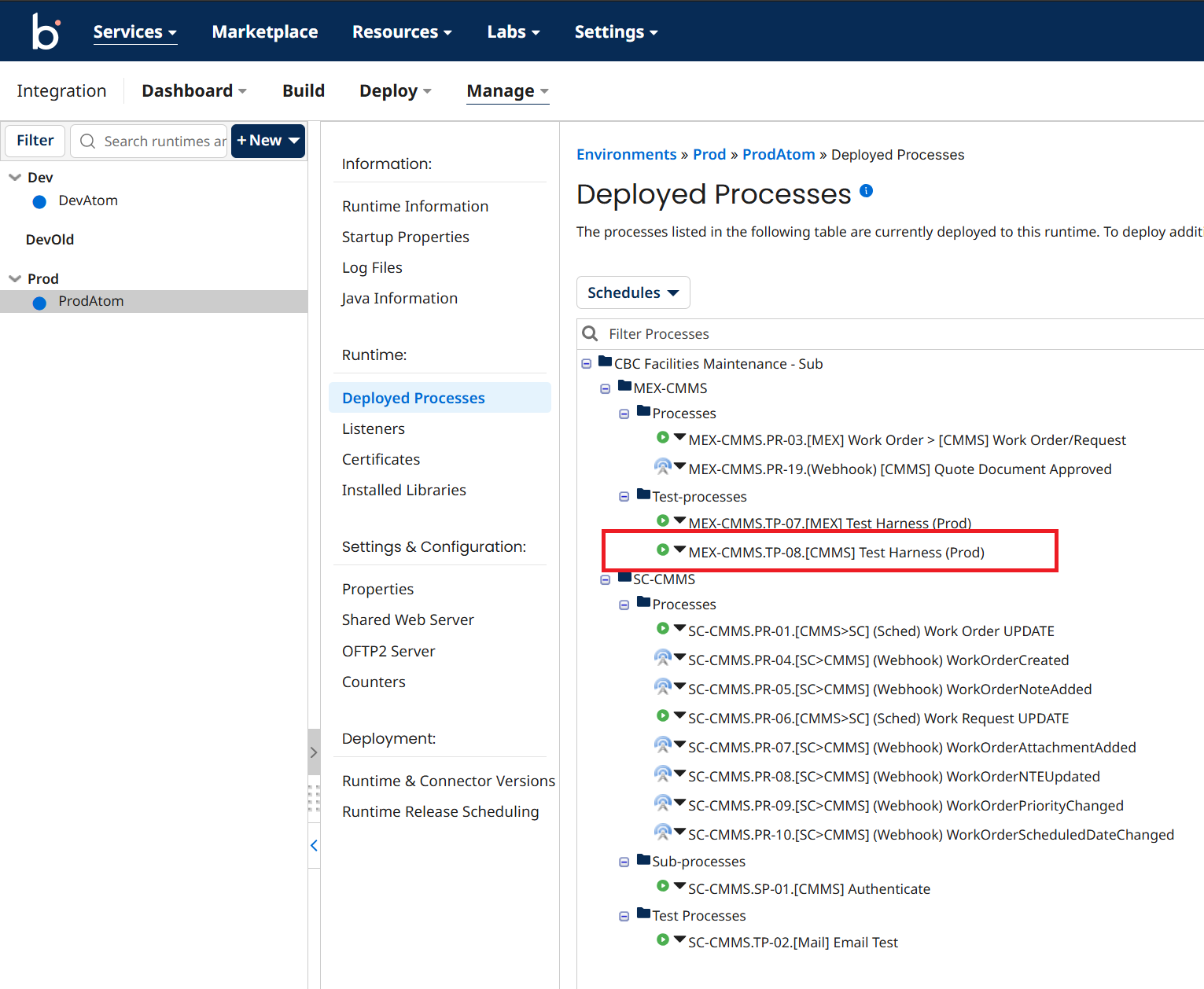
-
Logon to Boomi, and as can be seen from below, there is test harness that can be run directly. The output should produce a http 200 response.
-
Take a screen capture as evidence
7.0 Rollback to a previous Production version
Select the Production APIm Instance



Import the Production Definition exported in 6.0 Migrate to Production.



Update Web Service URL Once Imported
- The Web Service URL for production should be https://cmms.cbcgroup.com.au (opens in a new tab)

Check the revision URL
- Ensure the URL is /public-api
- Current is ticked
- APIm allows multiple versions. Each version can be reached by addressing the appropriate revision by adding ;rev=xx where xx is the revision. ie. /public-api;rev=53 (this will be the end point for revision 53)
It is important that the current API has NO rev=xx where xx is the revision. ie. /public-api ONLY
