MOR-PROC-xxx Version 1 Last Review Date: May, 2025
Database Scaling
Considerations
- Azure database costings are either Vcore or DTU based.
In DTU-based SQL purchase models, a fixed set of resources is assigned to the database or elastic pool via performance tiers: Basic, Standard, and Premium. This model is best for customers who prefer the simplicity of fixed payments each month, where the simplicity of pre-configured options is desired.
A vCore-based purchase model is best if you are looking for flexibility, control and transparency of individual resource consumption. This model allows you to scale compute, memory, and storage based upon your workload needs and provides a straightforward way to translate on-premises workload requirements to the cloud.
CMMS databases are all based on the DTU model.
Below are the steps required to manually alter the DTU assignment to a database.
It is important to note that depending on your server tier, the value of DTU's can only be set to certain values. For Example, on the Premium tier, the lowest DTU setting is 125, and can only go up to a value that is double its last. 125, 250, 500 etc.
On the Standard Tier, the lowest DTU setting is 10, and can be increased to the following values. 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 400, 800, 1600, 3000.
Method
Select Database Resource in the Azure Portal
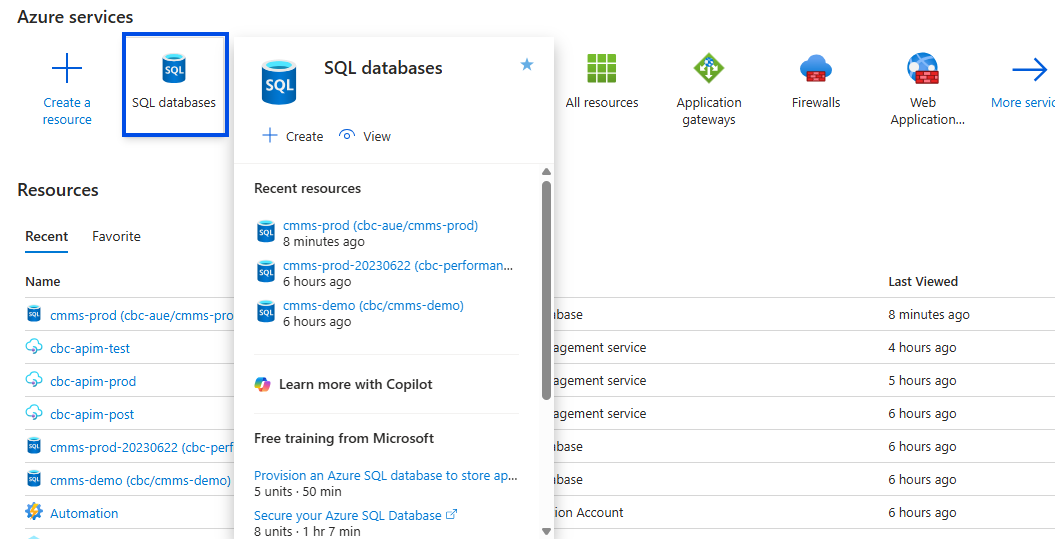
Select the Desired Database
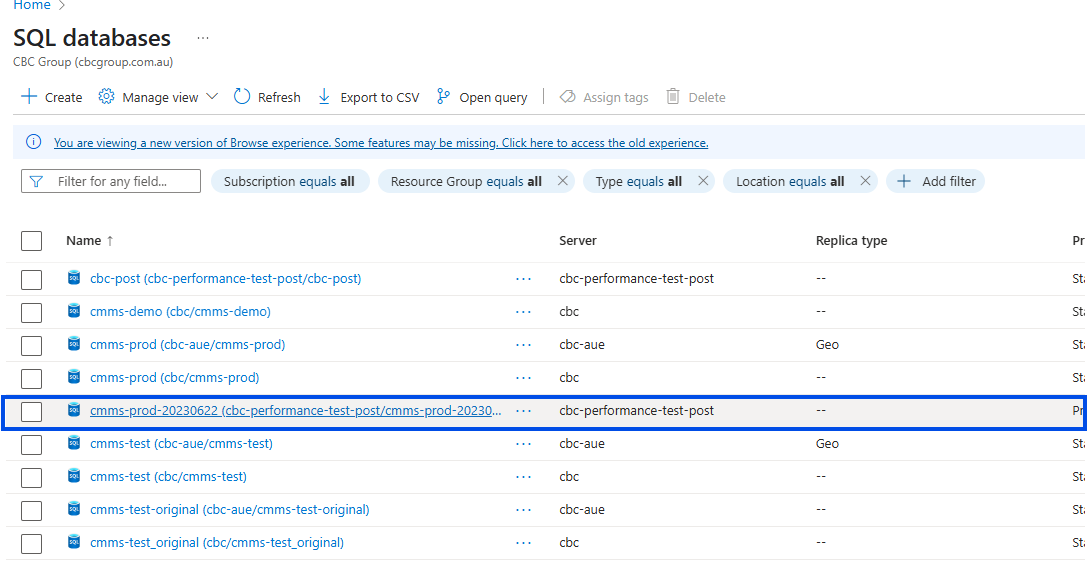
Select the Compute and storage Menu on the left
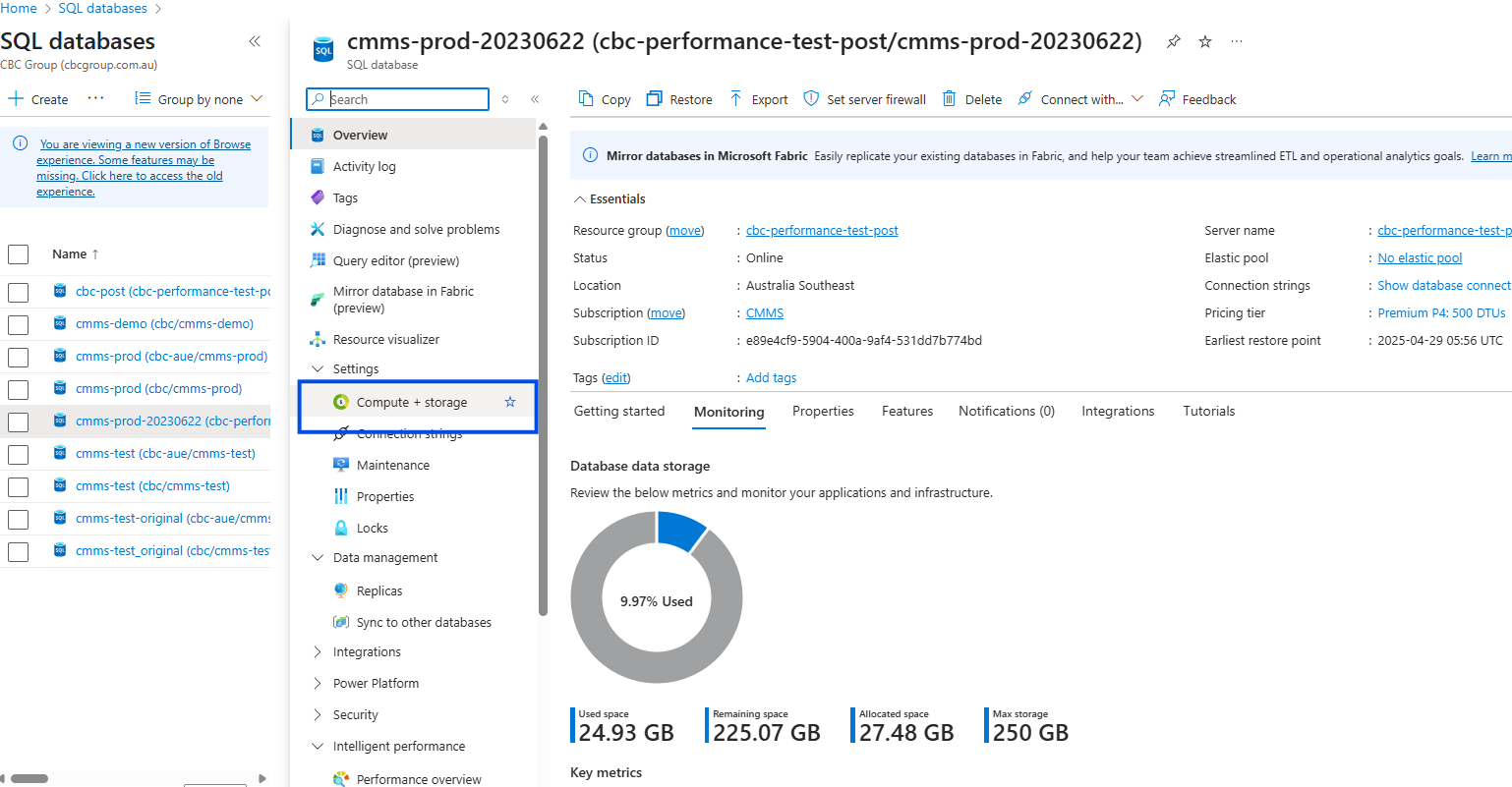
Service and Compute Tier Details
- You should now be able to see the details of the Service tier and the DTU settings.
- As mentioned above, the service tier setting will influence the upper and lower limts of DTU settings
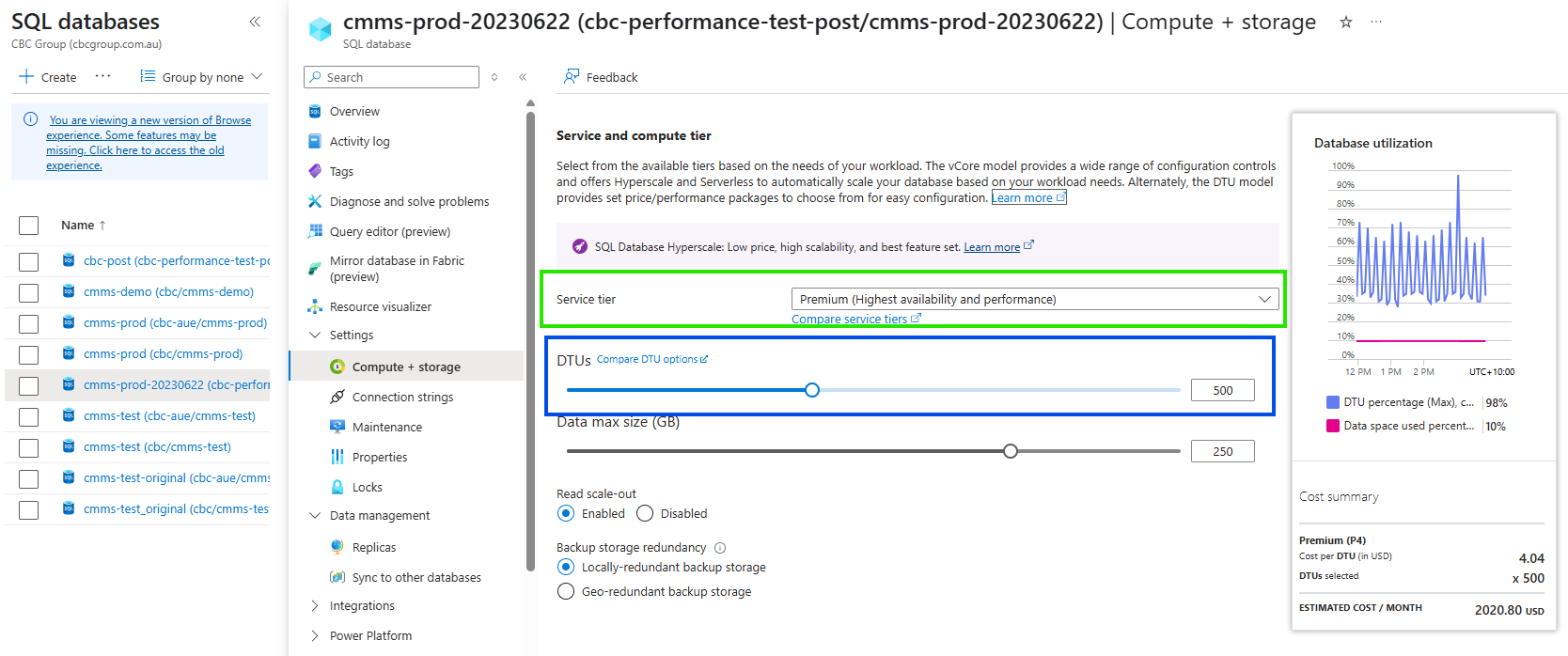
What Service Tier should we use?
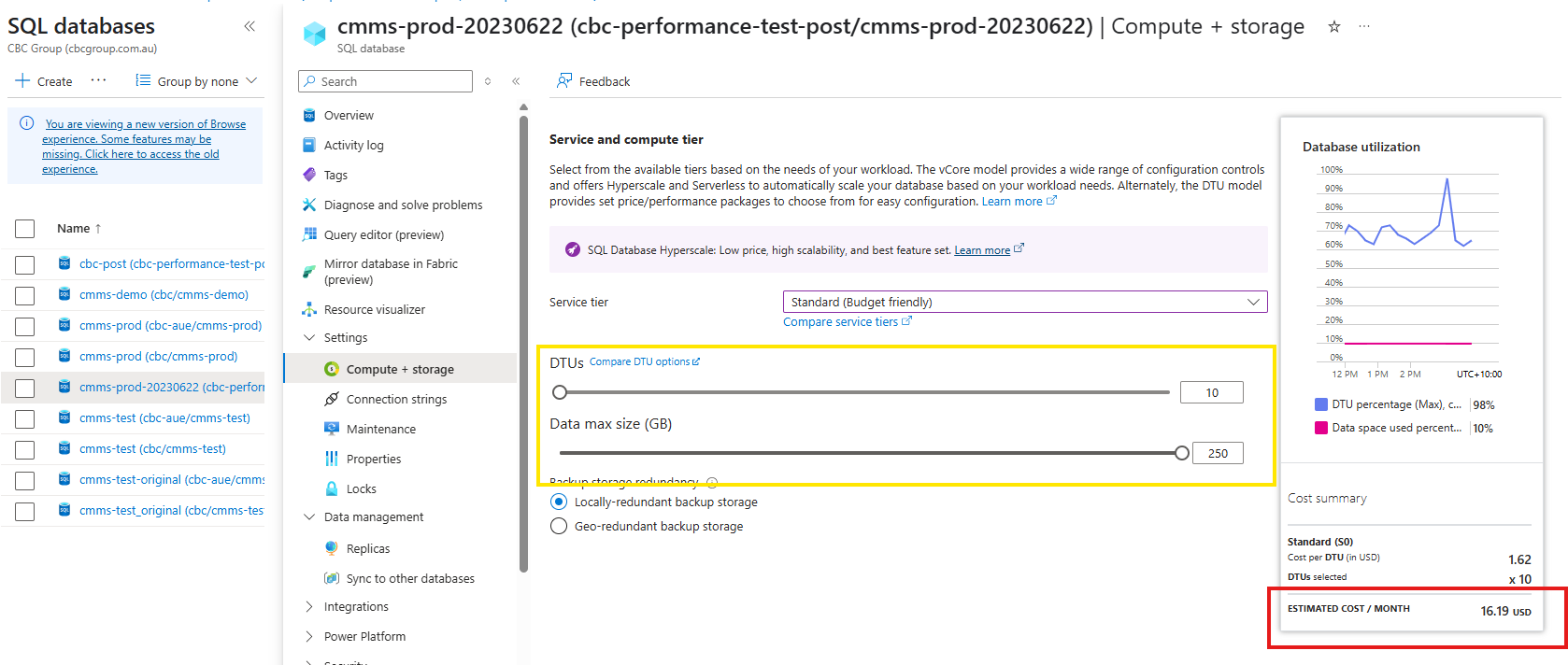
- If we are wanting to lower the DTU's in order to save money especially during night time when no or very little activity should be done, setting the service tier to Standard will allow a better price point. ie. DTU's can be set to 10 for example.
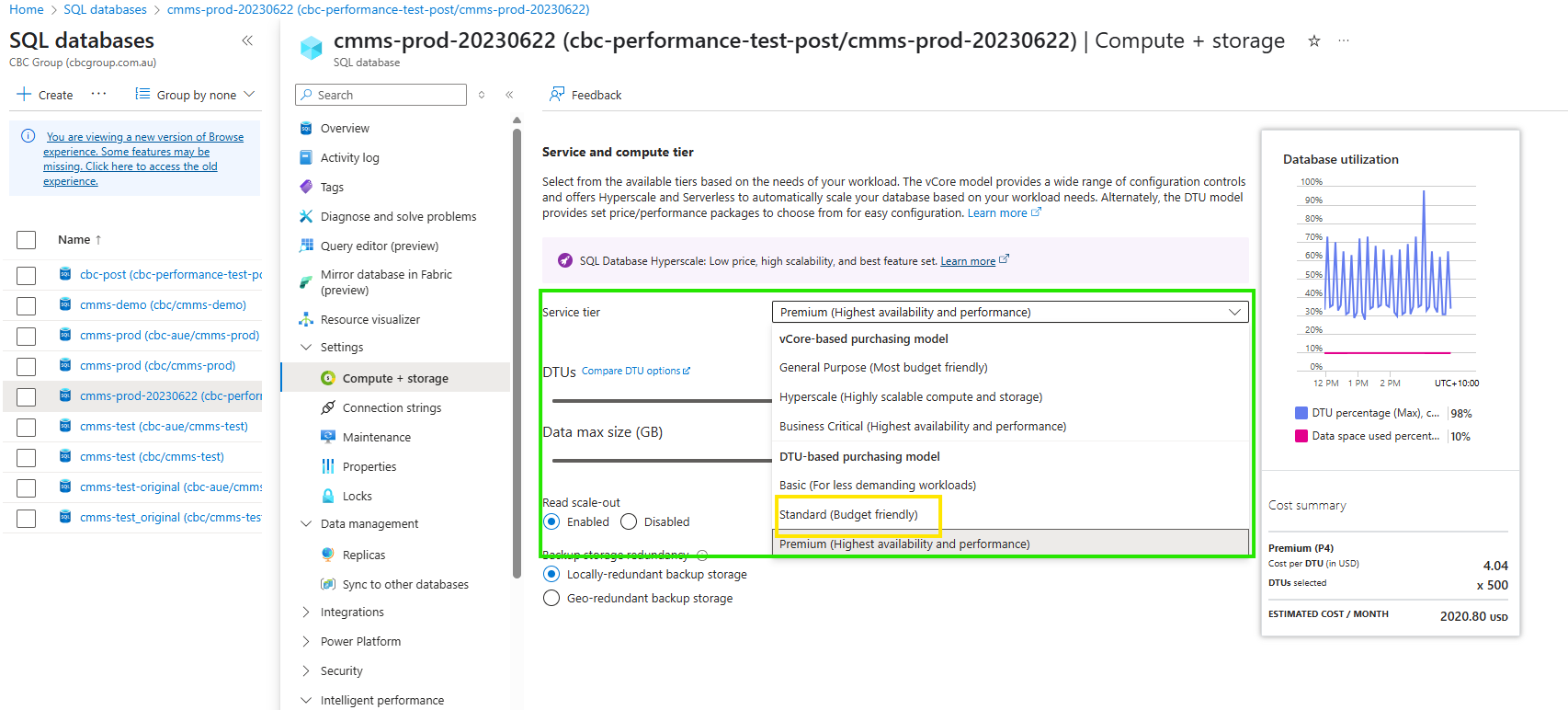
Set the desired DTU's
- use the slider to select the desired number of DTU's.
- It is important and recommended that the Data max size does not change. In the example shown, this is 250, and what ever tier you select, and DTU's, please ensure this value remains.
Script to change Database DTU setting
param(
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string] $resourceGroupName,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string] $serverName,
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string] $databaseName,
[parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string] $newServiceObjective = "S0"
)
# Set variables- using paramaters instead of static parameters
## $resourceGroupName = "YourResourceGroupName"
## $serverName = "YourServerName"
## $databaseName = "YourDatabaseName"
## $newServiceObjective = "S1" # Example: Change to Standard S1 tier
## see https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/resource-limits-dtu-single-databases?view=azuresql for all available values
# Get the database object
$database = Get-AzSqlDatabase -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -ServerName $serverName -DatabaseName $databaseName
# Update the service objective (DTUs)
$database | Set-AzSqlDatabase -RequestedServiceObjectiveName $newServiceObjective
# Verify the change
Get-AzSqlDatabase -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -ServerName $serverName -DatabaseName $databaseName | Format-List Name, ServiceObjective
Creating Azure RunBook
Setting up a Schedule
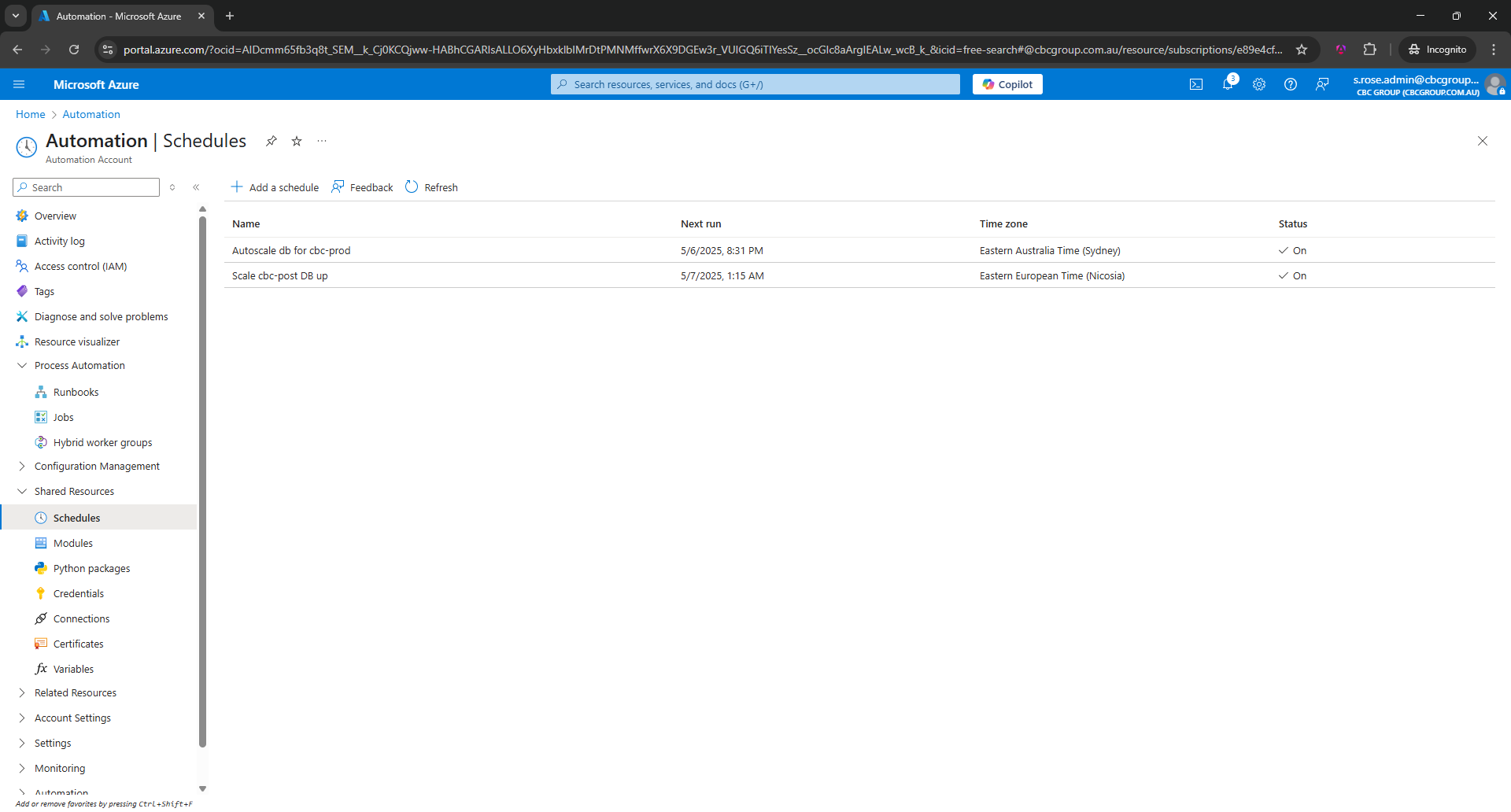
Link a RunBook to a Schedule