MOR-PROC-021 Version 1 Last Review Date: Nov, 2024
Restore an Azure SQL Database via PIT backup
1. Failure Scenario
This recovery plan relates to the following Failure Scenarios:
| Failure Scenario ID | Title | Link |
|---|---|---|
| 5B | Database Corruption | Link |
2. Backup Components
| Backup ID | Environment | Resource Type | Resource | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TBC | Prod | Azure SQL Database PITR backup | cmms-prod | SR to add link |
| TBC | Test | Azure SQL Database PITR backup | cmms-test | SR to add link |
3. Required Credentials and Permissions
| Environment | Service | Credential | Location | Permission |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prod | Azure Portal | Ability to modify prod database resources. | ||
| Prod | SQL Server (Primary) | NA | IP is in SQL Server whitelist. | |
| Prod | SQL Server (Secondary) | NA | IP is in SQL Server whitelist. | |
| Test | Azure Portal | Ability to modify test database resources. |
4. Required Software
| Software | Purpose | Notes | Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) | Perform database updates | ||
| Browser | Perform Azure Portal steps | NA |
5. Recovery Procedure
Backup and Restore
- Check backups: Azure provides automated backups (for services like Azure SQL Database). Verify that you have a recent backup of the database, which can help you restore it to a working state.
Use Data Recovery Options
- Azure SQL Database Point-in-Time Restore: If your Azure SQL database is corrupted, you should perform a point-in-time restore to revert to a time before the corruption occurred.
How To Restore SQL Database in Azure Portal
1. Navigate to https://portal.azure.com/#home (opens in a new tab)

2. Click the "Search resources, services, and docs (G+/)" field.

3. Type "sql"
4. Click "SQL databases"

5. Click "cmms-test (cbc/cmms-test)"

6. Click "Restore"

7. Click here - Select a Date and Time that you are confident the corruption had not occurred.

8. Select an Appropriate Date & Time to Restore from

9. Click here.

10. Click "Review + create"

11. Click "Create"

turn off Geo Replication
1. Navigate to https://portal.azure.com/#view/HubsExtension/BrowseResource/resourceType/Microsoft.Sql%2Fservers%2Fdatabases (opens in a new tab)

2. Click the "Search resources, services, and docs (G+/)" field.

3. Type "sql"
4. Click "SQL databases"

5. Click "cmms-test (cbc/cmms-test)"

6. Click "Replicas"

7. Click here.

8. Click this icon.

9. Click here.

10. Click here.

Rename the Original Database
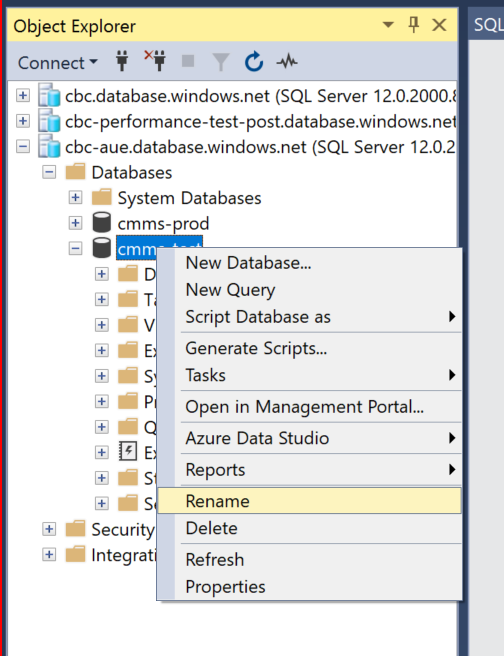
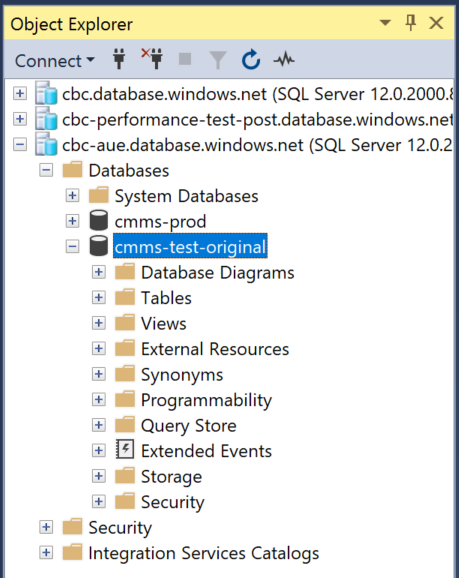
Rename the newly created database to Original Name


Rename the old Geo replicated Database


turn on Geo replication
1. Navigate to https://portal.azure.com/#home (opens in a new tab)

2. Click the "Search resources, services, and docs (G+/)" field.

3. Type "sql"
4. Click "SQL databases"

5. Click "cmms-test (cbc/cmms-test)"

6. Click "Replicas"

7. Click here.

8. Click "Toggle"

9. Click here.

10. Click "Review + create"

11. Click "Create"

Rebuild the Database (if needed)
- If you can't recover the database or the corruption is beyond repair, consider rebuilding the database from scratch, using any available backups or exports.
Key Points to Remember:
- Restore from backup is usually the most effective way to resolve database corruption.
- Run diagnostic checks to identify the scope of the corruption.
- Contact Azure support if you're unable to resolve the issue using available tools and methods.